United States economic powerhouse – Caribbean News Global
The United States has a diverse, highly developed and private-sector-led economy, which is the largest in the world in nominal GDP terms and is characterized by high levels of productivity, technological innovation, and competitiveness. Other key economic strengths include a flexible labor market, relatively solid demographics compared to other rich nations, and the use of the dollar – world’s reserve currency.
US economic data is strong: In the decade to 2022, the United States boasted real GDP growth of 2.1 percent, well above the G7 average of 1.7 percent. However, the US also has its weaknesses. Income inequality is the highest among its peers, politics and society at large are bitterly polarized, and the fiscal position is weak.
A bustling business environment
The country boasts many of the world’s largest and most successful corporations. The technology sector, centered in places like Silicon Valley, has played a pivotal role in driving innovation and global competitiveness. In recent decades, the United States has seen a shift towards a service-based economy, benefitting from a vast domestic consumer base. Services, such as finance, healthcare, education, and entertainment, now account for a substantial portion of GDP and employment.
Trade hub
International trade is a cornerstone of the US economy, with the nation being both a major importer and exporter of goods and services. That said, trade policy has turned more protectionist in recent years, with the country pulling out of talks to join the CPTPP trade agreement and locked in a trade and technology war with China.
Increasing government intervention
Under president Biden, the country has implemented a more state-led approach to economic management that focuses on boosting domestic manufacturing and ensuring the security of supply chains. Initiatives have included green-energy subsidies and tax breaks, fiscal incentives for semiconductor production, and domestic content requirements for government procurement.
Challenges
Income inequality, volatile politics and a mounting fiscal burden remain economic drags. Additionally, despite its active role in trade, the US has maintained a trade deficit for several decades. Moreover, climate change, healthcare costs, and the aging population pose long-term economic concerns.
US economic outlook
When looking at the United States’ economic forecasts, our analysts expect the nation’s outperformance relative to other major economies to continue over our forecast horizon. Economic diversification provides stability and resilience, helping the economy weather challenges such as economic downturns and global crises.
The United States’ economy in numbers
- Nominal GDP of USD 25,744 billion in 2022.
- GDP per capita of USD 77,187 compared to the global average of USD 10,589.
- Average real GDP growth of 2.3 percent over the last decade.
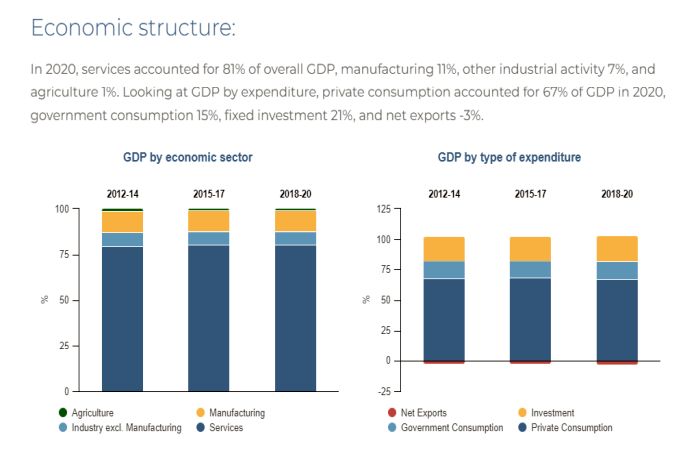
Economic structure
In 2020, services accounted for 81 percent of overall GDP, manufacturing 11 percent, other industrial activity 7 percent, and agriculture 1 percent. Looking at GDP by expenditure, private consumption accounted for 67 percent of GDP in 2020, government consumption 15 percent, fixed investment 21 percent, and net exports -3 percent.
International trade
In 2021, manufactured products made up 58 percent of total merchandise exports, mineral fuels 16 percent, food 11 percent, ores and metals 4 percent and agricultural raw materials 2 percent, with other categories accounting for 9 percent of the total. In the same period, manufactured products made up 77 percent of total merchandise imports, mineral fuels 8 percent, food 7 percent, ores and metals 3 percent and agricultural raw materials 1 percent, with other goods accounting for 4 percent of the total. Total exports were worth USD 2,090 billion in 2022, while total imports were USD 3,273 billion.
Question and Answers
- Why is the US economy so strong?
Primarily due to institutional stability, abundant natural resources, a culture of innovation, and a highly skilled workforce. The US dollar’s role as the world’s reserve currency also attracts global investment and facilitates government borrowing. Furthermore, the US has highly developed and flexible financial markets, world-leading technology companies, and top-tier universities.
- What are the US’ key economic weaknesses?
Yawning income inequality risks social and economic instability. Moreover, growing public debt could limit fiscal options. Additionally, the US has aging infrastructure- hence the USD 1 trillion infrastructure bill approved in 2021. Healthcare is costly and inefficient, and there is a mismatch between workers’ skills and those demanded by employers.
- Will China’s economy overtake the US economy?
Our analysts expect China’s economy to become larger than the US economy in nominal GDP terms in the 2030s, though China’s economy is already the largest when adjusting for the cost of living. However, there are multiple downside risks to China’s economy which could stop it from overtaking the US.
Source: caribbeannewsglobal.com