Developed countries materially surpassed their USD 100B climate finance commitment in 2022 – OECD
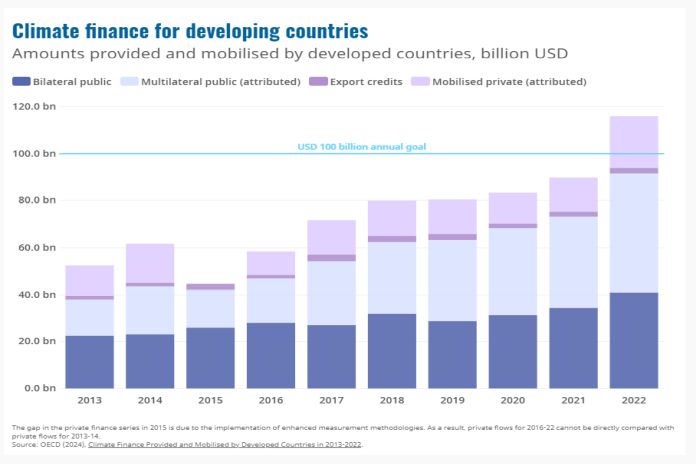
PARIS, France – Developed countries provided and mobilised USD 115.9 billion in climate finance for developing countries in 2022, exceeding the annual 100 billion goal for the first time and reaching a level that had not been expected before 2025.
According to new figures from the OECD, in 2022 climate finance was up by 30 percent from 2021, or by USD 26.3 billion. This is the biggest year-on-year increase to date and means that the 100 billion mark was reached a year earlier than the OECD had previously projected, albeit two years later than the initial target date of 2020.
Climate Finance Provided and Mobilised by Developed Countries in 2013-2022 is the OECD’s seventh assessment of progress towards the UNFCCC goal, agreed in 2009, of mobilising USD 100 billion a year by 2020 – a commitment later extended through to 2025 – to help developing countries mitigate and adapt to climate change. It comes as UNFCCC discussions are underway to set a New Collective Quantified Goal (NCQG) on climate finance for the post-2025 period, taking into account developing countries’ needs and priorities as well as the evolving global economic landscape.
“It is good to see that developed countries have exceeded the USD 100 billion goal in 2022. Exceeding this annual commitment materially by more than 15 percent is an important and symbolic achievement which goes some way towards making up for the two-year delay, which should help build trust. We encourage developed countries to keep up the momentum, also to leverage it further with additional policy efforts to boost private climate finance,” OECD secretary-general Mathias Cormann said.
“It will be important to sustain this level of elevated support through to 2025 while also increasing our ambition for the new post-2025 goal. Multilateral providers and the private sector will be key to further bridging the investment gap, notably in areas such as clean energy, agriculture and resilience. For the post-2025 period, the scope and design of the New Collective Quantified Goal on climate finance must be more comprehensive and effective than the existing goal by optimising the roles of different actors, finance sources, and policy incentives in order to address the scale and range of climate-related finance needs.”
Additional OECD analysis published this week highlights the need for the NCQG on climate finance to reflect and incentivise contributions from a broad range of sources in line with the scale of investment needed to achieve the Paris Agreement’s goals. The report explores ways the new goal could incorporate elements relating to public interventions that can either directly finance climate action or help mobilise private climate finance. It also discusses options for factoring in elements related to the quality of finance, as well as addressing key issues faced by developing countries such as access to finance and the sustainability of debt.
The 2022 climate finance data shows that public funds, from both bilateral and multilateral channels, continue to make up the bulk of climate finance, accounting for 80 percent of the total. Over the period recorded, multilateral public climate finance showed the biggest rise, up by USD 35 billion or 226 percent since 2013. The 2022 growth in public climate finance was accompanied by a jump of 52 percent or USD 7.5 billion, in mobilised private finance, which reached USD 21.9 billion in 2022 after several years of relative stagnation.
The figures also show an uptick in climate finance destined for adaptation action. Following a small drop in 2021, adaptation finance reached USD 32.4 billion in 2022, three times the 2016 level. The amount of public adaptation finance tracked by the OECD in 2019 was USD 18.8 billion and USD 20.3 billion with mobilised private finance included. Based on these figures, in 2022, developed countries were about halfway towards meeting the 2019 COP26 Glasgow Climate Pact’s call to double the provision of adaptation finance by 2025.
As with previous OECD assessments, this year’s edition provides insights relating to financial instruments as well as geographical distribution of climate finance. It shows that loans continue to represent the lion’s share of public climate finance, especially for multilateral development banks that typically finance large infrastructure projects, although grants are being prioritised in lower-income countries. The mix is more balanced for multilateral climate funds and bilateral providers, owing to a larger and more diverse range of activities and projects. Between 2016 and 2022, grants increased by USD 13.4 billion (more than doubling with an increase of 109%) and public loans by USD 30.3 billion (up 91%).
Climate finance to low-income countries remained relatively low at 10% in 2022. Importantly, however, least developed countries (LDCs) and small island developing states (SIDS), benefitted from a larger amount of finance for adaptation (about 50%) than the average for all developing countries (25%). On the other hand, private mobilised finance for LDCs and SIDS was very limited, underscoring the need for tailored international support to help address the challenges faced by these countries in attracting private investment for climate action.
The OECD will continue to track the fulfillment of the USD 100 billion goal through to 2025 as well as, pending the outcome of COP29 in Baku, contributing to international efforts to implement the NCQG in an effective way.
Related Links:
Source: caribbeannewsglobal.com