A better, safer egg decontamination
Glacier FarmMedia – Researchers at the University of Saskatchewan say a technique used for cleaning swine barns has led them to an effective method for decontaminating eggs.
Read Also


Ross Annett, gentleman auctioneer, retires
Colleagues, friends and family describe Ross Annett as professional, dedicated, loyal and a man of integrity. He received a standing…
Why it matters: The technique is more eco-friendly than current chemical methods of egg decontamination, making it an option for future commercialization.
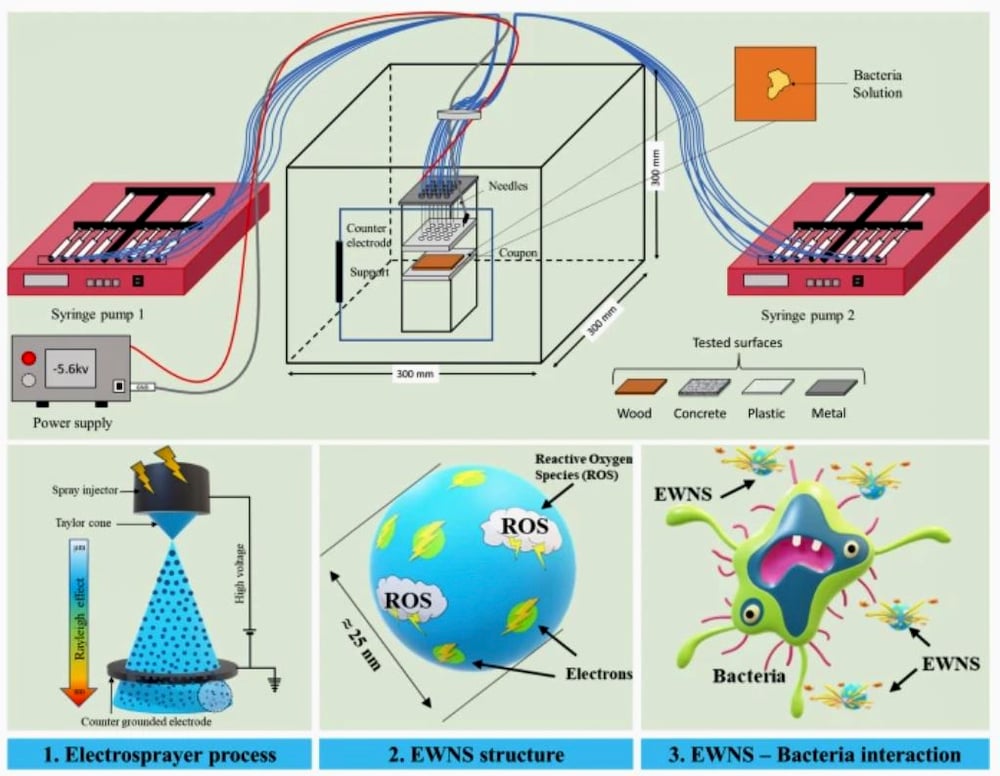
The method uses water and electricity to create engineered water nanostructures (EWN), which clean the eggs without damaging the cuticle, the natural outer coating that seals the egg. This reduces the need for refrigeration. Researchers say the method is 97.6 per cent effective against E. coli and 80.4 per cent effective against salmonella.
Mehdi Heydari Foroushani, a post-doctoral research fellow at the university’s college of engineering, said the process starts with imposing “a powerful electric field between needles and a ground while we have water inside these needles.
“This powerful electricity causes the water to start to be sprayed in small, nano sizes.”
The nano water molecules are rich in electrons and contain reactive oxygen. The oxygen and water interact with the microorganisms of bacteria, stopping them in their tracks, he said.
“This device has 16 needles and each needle uses one microlitre per minute of water flow. So, in total, we use 16 microlitres per minute for the device, a really low amount of water. It’s nothing really, just a droplet of water in a minute.”
A microlitre is one thousandth of a millilitre.
The method also uses less energy than current and experimental methods such as cold , Heydari Foroushani said.
The research team found the process is most effective when EWN is dispered onto the eggs at a current of nine kilovolts per centimetre for five minutes.
That’s a potential stumbling block if the process is commercialized, he acknowledged. Large egg facilities rely on quick methods. Overcoming that hurdle will be the next research step.
Safer eggs
The method was tested and observed at the Canadian Light Source at USask using the X-ray micro-computed tomography beam, which allowed the team to monitor safety of the egg cuticle. Eggshells are porous and the cuticle, invisible to the naked eye, seals those porous channels.
“The important thing here is that whenever we use any methods to decontaminate the egg surface, we want to make sure that we’re not damaging these materials, because these materials can control the gases exchange with the eggs and they are the first line of defence against micro-organisms’ penetrations inside the eggs.”
The team placed the egg in the synchrotron’s beam to create a high-resolution image of the shell at the microscopic level, allowing researchers to see the cuticle and any breaks. They found no change or damage. Compared to the typical chemical-water wash used commercially, this method is safer for the egg, said Heydari Foroushani.
“The washing of the eggs kind of damages these cuticles on the egg’s surface. We wash out these layers a little bit. That’s why after washing, we usually refrigerate the eggs. So, there is no need to put it in the refrigerator after using this methodology.”
Source: Farmtario.com