The Bank of Mexico has verified that Mexican fruit and vegetable exports to the United States have an impact on the prices of these products in the domestic market. The Bank’s first quarterly report for 2021 concluded that volatility in exports is a source of significant fluctuations in the local prices of some species.
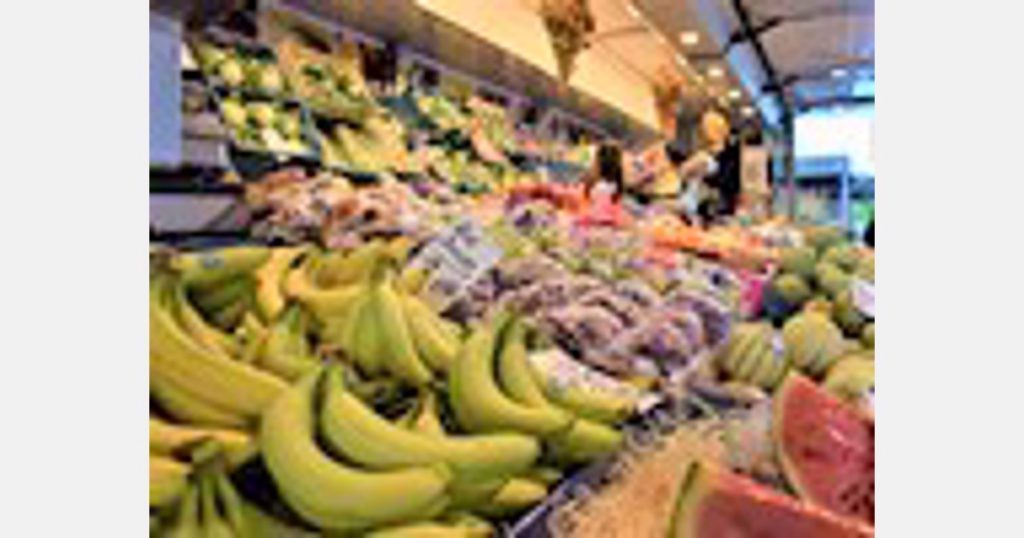
The study was carried out with some products that have an important weight in the country’s price index and in the commercial exchange between both countries, such as tomato, onion, chili, lettuce, avocado, lemon, pineapple, and banana.
According to the results of the report, a 1% increase in tomato exports to the United States would be associated with a 1.4% increase in the price index in the domestic market, while a 1% increase in onion and lemon exports would lead to a 1.7% and 1.8% increase in the domestic market, respectively. However, the product that is most sensitive to this phenomenon is the banana, as its prices can increase by 2.1% in Mexico if its exports rise by 1%.
There were also increases in the rest of the products: 1% in pineapple, 0.7% in chili peppers, 0.5% in lettuce, and 0.4% in avocado.
Banxico concluded that these findings have implications for understanding the dynamics of non-core inflation in Mexico. The trade relationship between Mexico and the United States had an impact on the prices of these agricultural products in Mexico and their behavior is difficult to predict because of their high volatility.
The Agrifood and Fisheries Information System (SIAP) constantly reveals in its daily monitoring reports that the increase in exports leads to an increase in the price of the products that remain in the national market.
Source: elfinanciero.com.mx